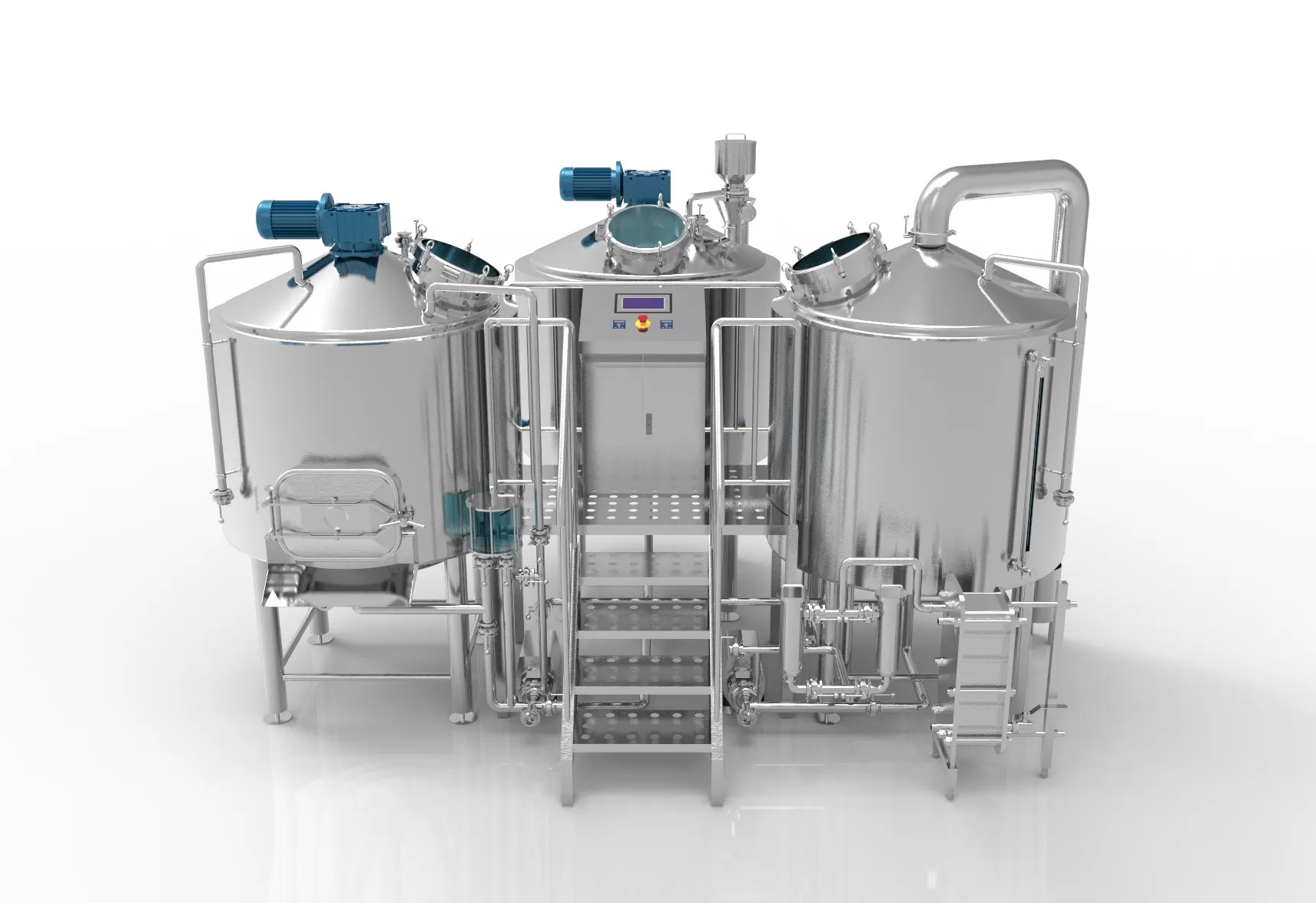
Craft-Bier hat in den letzten Jahren einen phänomenalen Aufschwung erlebt, denn Bierliebhaber suchen nach einzigartigen Geschmacksrichtungen und handwerklich hergestellten Bieren. Hinter jeder erfolgreichen Craft-Brauerei steht eine Reihe von Spezialgeräten, die den Anforderungen dieser ständig wachsenden Branche gerecht werden. In diesem Artikel tauchen wir in die Welt der Mikrobrauereianlagen ein und erforschen die verschiedenen Typen, die wichtigsten Komponenten, die Faktoren, die bei der Auswahl der richtigen Anlagen zu berücksichtigen sind, und vieles mehr. Also, schnappen Sie sich ein kaltes Bier und lassen Sie uns auf diese Reise gehen Kleinbrauerei Ausrüstung!
Was ist eine Mikrobrauereiausrüstung?
Bevor wir in die Details eintauchen, ist es wichtig zu verstehen, was Mikrobrauereianlagen sind. Einfach ausgedrückt, handelt es sich bei der Ausrüstung von Kleinstbrauereien um die Maschinen und Werkzeuge, die bei der Herstellung von Craft Beer in kleinem Maßstab verwendet werden. Im Gegensatz zu kommerziellen Großbrauereien konzentrieren sich Kleinstbrauereien auf die Herstellung begrenzter Biermengen und legen dabei den Schwerpunkt auf Qualität und Experimentierfreude.
Arten von Mikrobrauereianlagen
Bei der Einrichtung einer Kleinbrauerei gibt es verschiedene Arten von Geräten, die für den Brauprozess unerlässlich sind. Hier sind einige der wichtigsten Ausrüstungen für Kleinbrauereien:
- Ausrüstung des Sudhauses: Das Sudhaus ist das Herzstück einer Kleinbrauerei, in dem der Brauprozess abläuft. Es besteht in der Regel aus mehreren Komponenten:
- Maischbottich: Ein Gefäß, in dem gemälzte Körner mit heißem Wasser vermischt werden, um beim Maischen Zucker zu extrahieren.
- Braukessel: Auch als Kochkessel bekannt, wird er zum Kochen der Würze und zur Zugabe von Hopfen verwendet.
- Heißwassertank: Er speichert das für den Brauprozess verwendete heiße Wasser.
- Whirlpool: Dient der Abtrennung des Heißtrubs (Bodensatzes) von der Würze nach dem Kochen.
- Ausrüstung für die Fermentation: Die Gärung ist ein entscheidender Schritt bei der Bierherstellung, bei dem die Hefe Zucker in Alkohol umwandelt. Die Ausrüstung für die Gärung umfasst:
- Gärbehälter: Gefäße, in denen die Würze vergoren wird und die Hefe Zucker in Alkohol und Kohlendioxid umwandelt.
- Brite-Tanks: Sie werden auch als Konditionierungstanks oder Reifungstanks bezeichnet und dienen der Nachgärung und Klärung von Bier.
- Ausrüstung zur Kühlung und Filtration von Würze: Nach dem Kochen muss die Würze abgekühlt und gefiltert werden. Diese Ausrüstung umfasst:
- Plattenkühler: Wärmetauscher, die die heiße Würze schnell abkühlen.
- Wärmetauscher: Geräte, die Wärme von der heißen Würze auf das kalte Wasser übertragen.
- Filtersysteme: Dienen der Klärung des Biers durch Entfernung von Feststoffen, Sedimenten und Trübungen.
- Ausrüstung für die Kellerei: Die Kellereiausrüstung dient der Lagerung und Reifung des Biers nach der Gärung. Sie umfasst:
- Reifungstanks: Gefäße, in denen das Bier für eine bestimmte Zeit gelagert wird, um die gewünschten Geschmacks- und Aromastoffe zu entwickeln.
- Fässer: Wird für die Reifung von Bieren in Fässern verwendet, die dem Bier durch das Holz einzigartige Aromen verleihen.
- Keg-Anlagen: Anlagen zum Abfüllen des Biers in Fässer, um es für den Vertrieb oder den Ausschank vorzubereiten.
- Verpackungsausrüstung: Die Verpackungsanlagen dienen der Abfüllung des Biers in Flaschen oder Dosen und seiner Vorbereitung für den Vertrieb. Sie umfassen:
- Flaschenabfüllmaschinen: Automatisierte Systeme zum Füllen und Verschließen von Flaschen.
- Dosenlinien: Anlagen zum Füllen, Verschließen und Etikettieren von Dosen.
- Etikettiersysteme: Maschinen, die Etiketten auf Flaschen oder Dosen anbringen.
- Kontrollsysteme: Mikrobrauereien verwenden häufig Kontrollsysteme zur Überwachung und Steuerung verschiedener Parameter des Brauprozesses, wie Temperatur, Druck und Zeitsteuerung. Diese Systeme gewährleisten Konsistenz und Präzision bei der Bierherstellung.
- Reinigungs- und Desinfektionsgeräte: Die Aufrechterhaltung von Sauberkeit und Hygiene ist in der Brauereiindustrie von entscheidender Bedeutung. Reinigungs- und Desinfektionsgeräte, einschließlich Reinigung vor Ort (CIP) Systemen, hilft bei der Beseitigung von Verunreinigungen und der Aufrechterhaltung hygienischer Bedingungen in der Brauereiausrüstung.
Dies sind einige der wichtigsten Ausrüstungen für Kleinbrauereien, die von den Brauern zur Herstellung von hochwertigem Craft Beer eingesetzt werden. Jeder Anlagentyp dient einem bestimmten Zweck im Brauprozess, und die Auswahl hängt von der Produktionskapazität der Brauerei und ihren spezifischen Brauerfordernissen ab.

Wesentliche Komponenten der Mikrobrauereiausrüstung
Die Ausrüstung einer Mikrobrauerei besteht aus verschiedenen wesentlichen Komponenten, die zum Brauprozess und zur allgemeinen Funktionalität der Brauerei beitragen. Diese Komponenten arbeiten zusammen, um die effiziente Herstellung von hochwertigem Craft Beer zu gewährleisten. Im Folgenden werden einige der wichtigsten Komponenten von Mikrobrauereianlagen vorgestellt:
- Kontrollsystem: Ein Kontrollsystem ist eine wichtige Komponente, die verschiedene Parameter während des gesamten Brauprozesses regelt und überwacht. Es umfasst Sensoren, Sonden, Regler und Software, die es den Brauern ermöglichen, Temperatur, Druck, Zeit und andere kritische Variablen zu verwalten und anzupassen. Das Kontrollsystem sorgt für Konsistenz und Präzision im Brauprozess.
- Pumpen: Pumpen spielen eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Bewegung von Flüssigkeiten in der Brauanlage. Sie sind für den Transfer von Würze, Bier, Reinigungslösungen und anderen Flüssigkeiten zwischen verschiedenen Behältern und Geräten zuständig. Es gibt verschiedene Arten von Pumpen, darunter Kreiselpumpen und Verdrängerpumpen, und ihre Auswahl hängt von den spezifischen Anforderungen des Brauprozesses ab.
- Heizungs- und Kühlungssysteme: Heiz- und Kühlsysteme sind für die Aufrechterhaltung einer präzisen Temperaturkontrolle während der verschiedenen Phasen des Brauprozesses unerlässlich. Zu diesen Systemen gehören Wärmetauscher, Heizkessel, Kühlanlagen und glycol systems. They enable brewers to heat the brewing water, control the temperature during mashing, cool the wort after boiling, and maintain fermentation temperatures within desired ranges.
- Grain Handling Equipment: Grain handling equipment is crucial for efficiently processing malted grains. This equipment includes grain mills, which crush the malted grains to expose the starches for extraction during mashing, and augers or conveyors, which help transfer the milled grains to the mash tun.
- Reinigungs- und Desinfektionsgeräte: Maintaining cleanliness and ensuring proper sanitization of brewing equipment is essential for producing high-quality beer. Cleaning and sanitization equipment includes Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems, which automate the cleaning process by circulating cleaning solutions through the brewing vessels and piping. This helps remove residual contaminants, yeast, and bacteria, ensuring hygienic brewing conditions.
- Gärgefäße: Fermentation vessels, such as fermenters and brite tanks, are where the wort undergoes fermentation and conditioning. These vessels are typically made of stainless steel and often equipped with temperature control systems, pressure relief valves, and sanitary fittings to create an optimal environment for yeast activity and beer maturation.
- Packaging Components: Packaging components are essential for the packaging and distribution of the finished beer. They include carbonation systems, filling valves, keg couplers, bottle or can fillers, and labeling systems. These components help package the beer into bottles, cans, or kegs while ensuring proper carbonation and maintaining product quality.
- Valves and Fittings: Valves and fittings are crucial for controlling the flow of liquids and gases within the brewing system. They include ball valves, butterfly valves, sample valves, sight glasses, and sanitary fittings. These components enable brewers to control the movement of fluids during various stages of the brewing process, such as transferring liquids between vessels, controlling flow rates, and taking samples for quality testing.
These are some of the essential components found in microbrewery equipment. Each component plays a critical role in the brewing process, ensuring efficiency, control, and hygiene throughout the production of craft beer. The selection and integration of these components depend on the specific needs and scale of the microbrewery.
Faktoren, die bei der Auswahl von Mikrobrauereianlagen zu berücksichtigen sind
When choosing microbrewery equipment, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure the equipment meets your brewing needs and supports the success of your microbrewery. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Production Capacity: Determine the desired production capacity of your microbrewery. Consider the volume of beer you aim to produce, both in terms of batch size and overall annual production. Choose equipment that can handle your projected production volume effectively.
- Quality and Efficiency: Invest in high-quality equipment that is designed for efficient and consistent performance. Look for reputable manufacturers known for their craftsmanship and reliability. Efficient equipment will help you optimize your brewing process, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Consider the flexibility and scalability of the equipment. Evaluate whether the equipment allows for future growth and expansion. Can it accommodate increasing production volumes or the addition of new beer styles? Choosing equipment that offers flexibility and scalability will enable you to adapt to changing market demands and brewery growth.
- Space and Layout: Assess the available space in your brewery and consider the equipment layout. Ensure that the equipment you choose fits within your allocated space and allows for efficient workflow and ease of operation. Consider the accessibility of the equipment for maintenance and cleaning purposes.
- Budget and Cost Analysis: Set a realistic budget for your microbrewery equipment. Consider not only the initial purchase cost but also the long-term cost of ownership, including maintenance, repairs, and utility expenses. Conduct a thorough cost analysis to understand the financial implications and ensure that your equipment investments align with your budget.
- Brewing Style and Complexity: Consider the specific brewing style and complexity of beers you intend to produce. Some equipment may be better suited for specific beer styles or brewing techniques. Ensure that the equipment you choose supports the brewing processes and techniques required for your desired beer profiles.
- Support and Service: Assess the level of support and service offered by equipment manufacturers or suppliers. Consider factors such as warranty, technical assistance, spare parts availability, and after-sales support. Reliable support ensures prompt assistance in case of equipment issues or breakdowns.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Consider the energy efficiency and sustainability features of the equipment. Energy-efficient equipment can help reduce utility costs and minimize environmental impact. Look for equipment that incorporates features like heat recovery systems, efficient insulation, and water-saving technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the equipment meets the necessary regulatory standards and complies with local health and safety regulations. Compliance with regulations ensures the safety of your operations and the quality of your beer.
- User-Friendliness and Training: Consider the ease of use and user-friendliness of the equipment. Equipment that is intuitive and user-friendly will streamline your brewing process and reduce the learning curve for your brewing team. Additionally, assess the availability of training resources and support to ensure that your team can effectively operate the equipment.
Wichtige Überlegungen zur Gründung einer Kleinbrauerei
Setting up a Kleinbrauerei requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Licenses and Permits: Obtain the necessary licenses and permits required by local authorities to operate a brewery. This may include permits for production, distribution, and serving alcohol.
- Location and Space: Choose a suitable location for your microbrewery, considering factors such as accessibility, zoning regulations, and proximity to your target market. Ensure the space is adequately ventilated, has proper drainage, and meets safety standards.
- Recipe Development and Experimentation: Craft beer enthusiasts appreciate innovation and unique flavors. Invest time in developing and refining your beer recipes, allowing room for experimentation and creativity.
- Marketing and Branding: Develop a strong brand identity and marketing strategy to promote your microbrewery. Utilize social media, online platforms, and local events to create awareness and attract customers.
- Staff and Training: Recruit a skilled team of brewers, cellar workers, and sales staff who are passionate about craft beer. Provide ongoing training to enhance their knowledge and skills, ensuring consistent quality in beer production.
By considering these key aspects, you can lay a solid foundation for your microbrewery and increase your chances of success in the competitive craft beer market.
Kostenanalyse der Mikrobrauereiausrüstung
Starting a microbrewery involves significant financial investment. Here is a cost analysis of key equipment and other expenses to help you plan your budget:
- Ausrüstung des Sudhauses: The cost of a brewhouse can vary depending on its size, configuration, and additional features. A small-scale brewhouse suitable for a microbrewery can range from $50,000 to $200,000. This includes the mash tun, brew kettle, hot liquor tank, and whirlpool.
- Ausrüstung für die Fermentation: Fermentation equipment, including fermenters and brite tanks, can cost between $10,000 and $50,000, depending on their size and specifications. Temperature control systems may require an additional investment of $5,000 to $20,000.
- Ausrüstung zur Kühlung und Filtration von Würze: Investing in plate chillers, heat exchangers, and filtration systems can cost around $10,000 to $30,000. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining the clarity and quality of the beer.
- Ausrüstung für die Kellerei: Cellaring equipment, such as aging tanks, barrels, and kegging systems, may range from $10,000 to $50,000. The cost will depend on the capacity and materials used.
- Verpackungsausrüstung: Packaging equipment, including bottling machines, canning lines, labeling systems, and packaging materials, can vary significantly in cost. A small-scale packaging setup can range from $10,000 to $50,000 or more, depending on the desired output capacity.
In addition to equipment costs, it’s important to consider other expenses, such as:
- Renovation and construction costs for the brewery space
- Utilities, including water, electricity, and gas
- Raw materials, such as malt, hops, yeast, and adjuncts
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Licensing and permit fees
- Insurance coverage for the brewery and equipment
- Ongoing maintenance and repairs
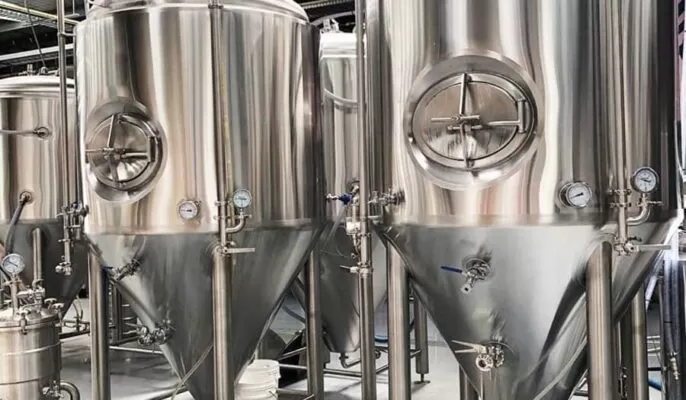

Vorteile der Verwendung hochwertiger Mikrobrauereianlagen
Using high-quality microbrewery equipment offers several benefits for brewers and their craft beer production:
- Consistent Quality: High-quality equipment ensures consistency in the brewing process, resulting in consistent flavor profiles and beer quality. Precise temperature control, efficient filtration, and reliable fermentation contribute to the overall consistency of the final product.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: High-quality equipment is designed to optimize efficiency and productivity. Advanced technology, such as automated controls and efficient heat transfer systems, allows brewers to streamline their operations, reduce manual labor, and increase output without compromising on quality.
- Improved Control and Flexibility: Top-notch equipment provides brewers with better control over various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. This level of control enables them to fine-tune their brewing processes, experiment with different recipes, and achieve desired flavors and aromas with precision.
- Durability and Longevity: Investing in durable, well-built equipment ensures longevity and reduces the risk of breakdowns or costly repairs. High-quality materials and craftsmanship contribute to the reliability and robustness of the equipment, allowing brewers to focus on their craft rather than equipment maintenance.
- Safety and Hygiene: Premium microbrewery equipment is designed with safety and hygiene in mind. It incorporates features such as sanitary fittings, easy cleaning access, and adherence to industry standards for food-grade materials. This helps maintain a clean, sanitary brewing environment and minimizes the risk of contamination.
By using high-quality microbrewery equipment, brewers can elevate their craft, produce exceptional beers, and build a solid foundation for long-term success in the competitive craft beer market.
Herausforderungen und Lösungen bei der Ausrüstung von Mikrobrauereien
Microbrewery equipment comes with its own set of challenges. However, with careful planning and proactive measures, these challenges can be overcome. Here are some common challenges in microbrewery equipment and potential solutions:
- Cost Constraints: Investing in microbrewery equipment can be a significant financial burden, especially for small-scale or startup breweries. To overcome this challenge, brewers can consider leasing options, seek financing partnerships, or opt for used equipment that meets their quality standards.
- Maintenance and Technical Expertise: Maintaining and troubleshooting complex brewing equipment requires technical expertise. Brewers can address this challenge by investing in training programs for their staff or partnering with equipment suppliers that provide comprehensive support and maintenance services. Regular equipment inspections and preventive maintenance can help identify and address issues before they become costly problems.
- Quality Control and Consistency: Maintaining consistent quality across batches can be challenging, especially for smaller breweries. Implementing strict quality control protocols, investing in automation and monitoring systems, and conducting regular sensory evaluations can help ensure consistency in taste, aroma, and overall beer quality. Standardizing processes and documenting recipes and brewing parameters can also contribute to consistent results.
- Scaling Production: As breweries grow and demand increases, scaling up production while maintaining quality can be a challenge. Brewers should plan for scalability from the start, ensuring that their equipment and infrastructure can handle increased volumes. Collaboration with experienced brewing consultants can provide valuable insights and assistance during this process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Microbreweries need to adhere to various regulatory requirements, including permits, licensing, health and safety standards, and labeling regulations. Staying informed about local, regional, and national regulations, and working closely with legal and compliance experts, helps ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
By proactively addressing these challenges and seeking appropriate solutions, brewers can optimize their microbrewery equipment’s performance, ensure consistent quality, and achieve sustainable growth in the competitive craft beer industry.