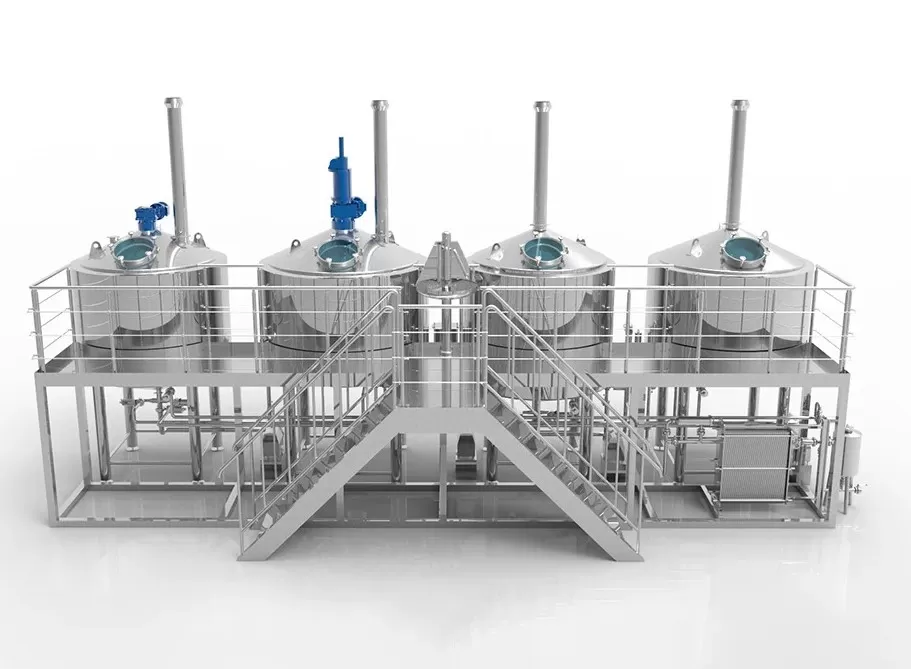
As consumer demand for natural and healthy beverages continues to grow, kombucha —a fermented tea beverage low in sugar and rich in probiotics and organic acids —is rapidly transitioning from a niche market to a mainstream one. According to the Global Kombucha Market Report, the global kombucha market is expected to exceed $10 billion by 2030. This trend has attracted numerous beverage brands and entrepreneurs to invest in kombucha production and distribution. However, industrial kombucha brewing is more than just a simple fermentation process; it is a systematic project requiring stringent process standards, sanitary conditions, and equipment performance. As a professional vybavení kombuchy manufacturer, we understand the importance of equipment selection for brewing quality, production efficiency, and scalability. This guide will focus on key equipment types, process flow, and equipment selection criteria required for kombucha brewing, helping companies make informed decisions when building kombucha plants.
Core Kombucha Brewing Process
Understanding the kombucha brewing process is the first step in choosing the right equipment. The basic kombucha brewing process typically includes the following key steps:
- Tea Brewing
- Sweetening and Cooling
- Primární kvašení
- Secondary Fermentation & Flavoring
- Filtration and Sterilization (optional)
- Packaging (canned/bottled)

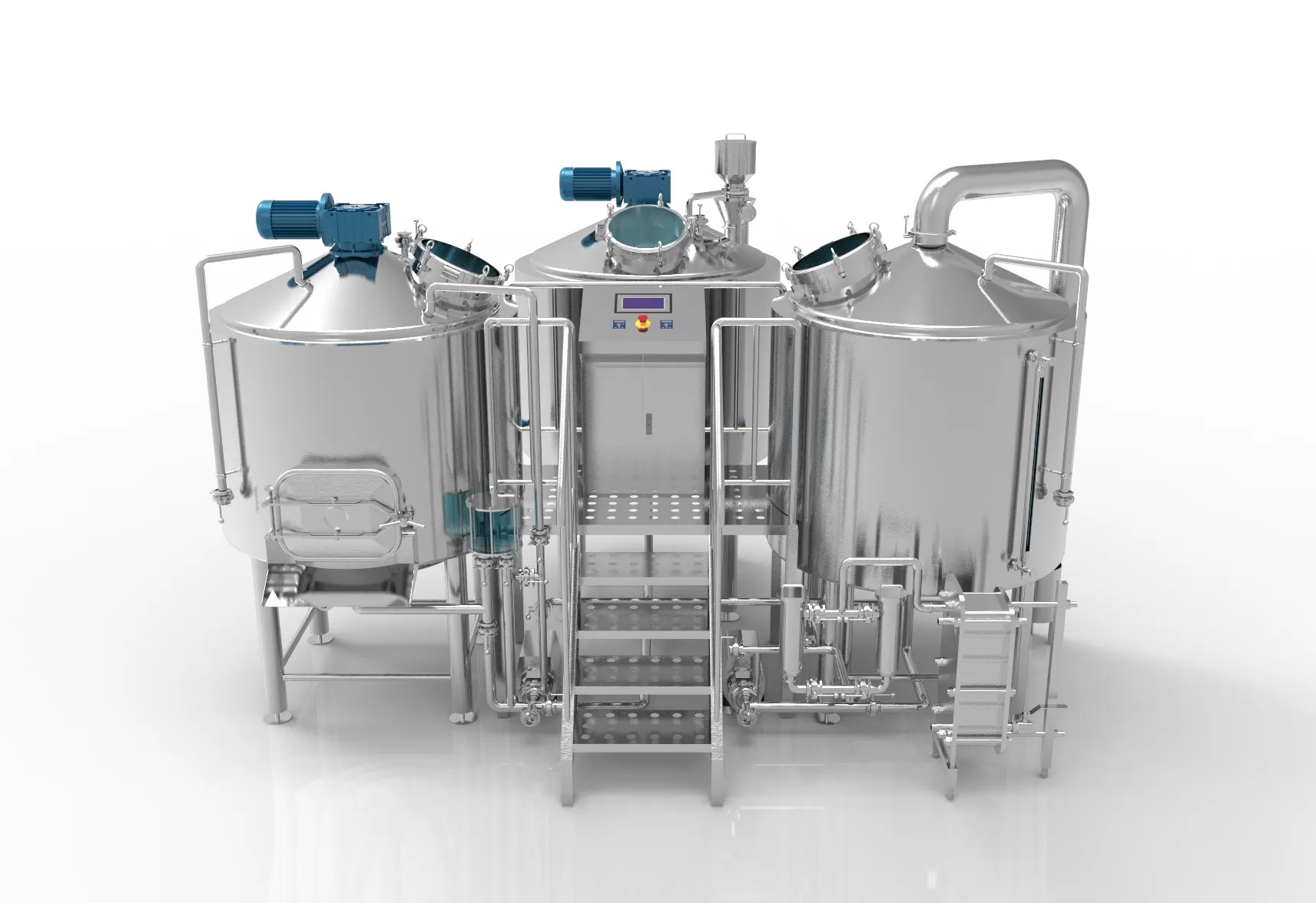
Key Equipment Types Required for a Kombucha Brewing Plant
Tea Brewing Kettle
- Function: Used to brew tea leaves with hot water and extract tea polyphenols.
- Recommended Material: Food-grade stainless steel 304 or 316L.
- Equipment Features: Automatic temperature control, stirring system, and explosion-proof design.
- Selection Recommendations: Consider production capacity (capacities ranging from 100L to 5000L are recommended) and whether a continuous tea production system is required.
Sweetener Mixing & Cooling Tank
- Function: Dissolves sugar in hot tea and quickly cools it to a suitable temperature for adding the culture solution (20–30°C).
- Configuration Recommendations: Equipped with automatic temperature control, cooling jacket, and agitator; a CIP cleaning system is recommended.
- Capacity Matching: Match the capacity of the tea brewing kettle to avoid cooling bottlenecks.
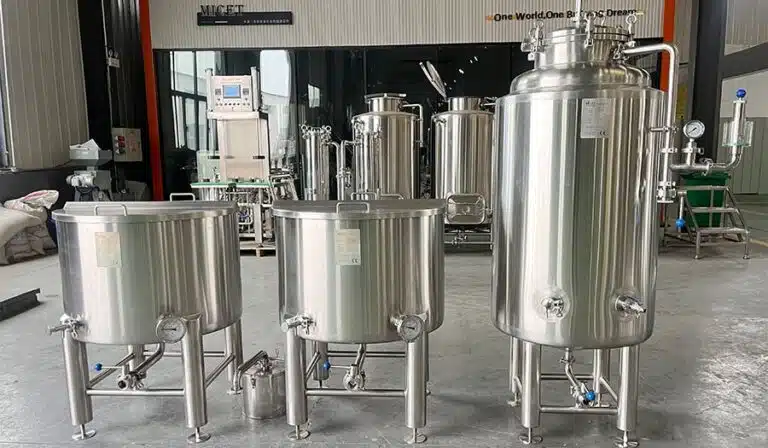
Fermentační nádrž
- Core equipment determines product quality.
- Recommended Type: Cylindrical vertical fermentační nádrž or conical bottom tank, open or closed.
- Key Parameters:
- Temperature control system (constant-temperature fermentation);
- Ventilation or gas exchange port (SCOBY requires oxygen);
- Food-grade interior polish to prevent contamination;
- Optional UV sterilizer and CO₂ exhaust device.
- Notes:
- Most breweries choose “static fermentation,” and the fermenter should be able to accommodate extended occupancy;
- Small equipment should consider space efficiency, while large equipment should be equipped with a SCADA data monitoring system.
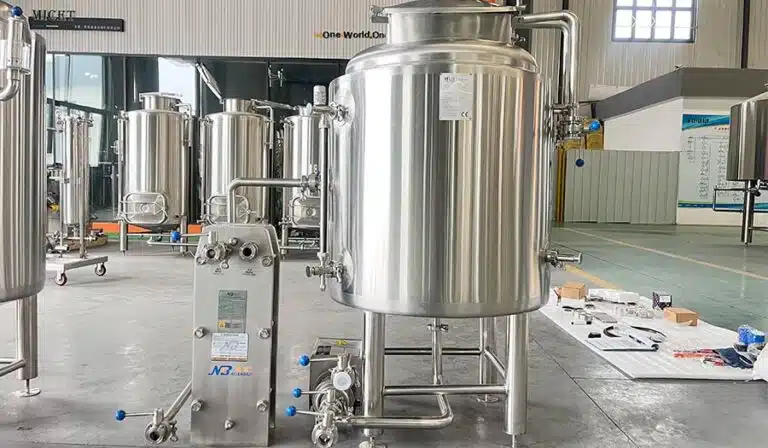
Filtration & Blending System
- Purpose: Filter out SCOBY residue; adjust pH, Brix (sugar content), and add flavors (juice/essential oil, etc.).
- Equipment Components:
- Multi-stage filtration system, membrane filter;
- Online pH meter, flow meter;
- Automatic batching pump and blending tank.
- Key Control Points: High hygiene standards must be maintained to prevent secondary contamination.

Filling & Capping Line
- Equipment Type: Glass bottle filling line; PET bottle/aluminum can plnicí systém; atmospheric or isobaric filling depending on whether the system contains gas.
- Selection Key Points:
- Support for small batches or trial filling;
- Seamless integration with sterilization or pasteurization systems;
- Does the filling speed meet daily production capacity requirements?
- Does it have automatic labeling and date coding capabilities?
Refrigerated Storage and Fermentation Room Temperature Control System
- Reason: Kombucha is very sensitive to temperature at different stages.
- Configuration Recommendations:
- Pre-fermentation room (constant temperature 22–27°C);
- Finished product warehouse (storage below 4°C);
- The temperature control system must be networked and equipped with humidity control.
Kombucha Equipment Selection Criteria and Considerations
Choose a scalable equipment combination based on capacity planning.
Kombucha brewing companies have varying capacity requirements at different stages of development, so equipment selection should offer modularity and scalability. For example, small plants can use 500L or 1000L fermenters for pilot production, while medium- to large-scale companies should deploy multiple interconnected 2000L–5000L fermentation units, creating a parallel production line layout. Importantly, equipment piping, control systems, and CIP stations must allow for expansion capacity to avoid the risk of duplication of investment and production downtime due to subsequent equipment replacements. Flexible configuration of main equipment and auxiliary systems can achieve a smooth transition from small-scale pilot production to large-scale production.
Ensure that equipment, materials, and construction meet food hygiene standards.
As a low-pH, highly active functional beverage, kombucha places extremely high demands on equipment for corrosion resistance, sealing, and sanitation. When selecting equipment, ensure that all parts that come into contact with the product are made of food-grade 304 or 316L stainless steel, with a mirror-polished interior and a roughness R value no higher than 0.6μm, to prevent bacterial growth and product residue. Furthermore, key interfaces such as valves, piping, and agitator shafts should feature sanitary, quick-release designs for easy disassembly, cleaning, and maintenance. GMP-compliant CIP (Cleaning in Place) and SIP (Sterilization in Place) systems are recommended to ensure quick and efficient cleaning after each batch, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination.
Emphasis on precise control of key parameters such as temperature, pH, and Brix.
Kombucha core fermentation process is highly sensitive to temperature, pH, and sugar content. Equipment systems must possess precise automated control and real-time monitoring capabilities to ensure consistent fermentation conditions from batch to batch. For example, fermenters should be equipped with high-sensitivity temperature probes, cooling jackets, or external temperature-controlled coils to maintain the optimal fermentation temperature range (22–27°C). The blending system should include a built-in pH sensor and Brix detection module, which, combined with automated dosing valves, allows for dynamic adjustments to ensure consistent flavor. Large breweries may consider implementing a SCADA system to enable remote monitoring, batch traceability, and historical process parameter query, thereby improving overall automation.

The selected filling system should be compatible with the product form and market positioning.
Kombucha products can be categorized as carbonated or static, and the corresponding filling processes differ significantly. Carbonated products require an isobaric filling system to prevent gas loss, while static products can be filled at atmospheric pressure. Companies should select a filling method based on their product positioning and comprehensively evaluate the bottle type (glass, PET, aluminum cans, etc.), production capacity (hourly filling volume), and functional requirements (whether labeling, coding, screw capping, etc.). Startups can use semi-automatic or all-in-one machines, while established brands should utilize fully automated high-speed filling lines to match their sales volume.
Balancing R&D flexibility and process diversity
In the ever-changing market, kombucha companies need to continuously develop new products, including low-sugar, high-fiber, herbal extracts, and fruit-flavored blends. Therefore, equipment should possess a certain degree of “process flexibility” to support varying fermentation times, blending processes, and flavor addition methods. For example, fermenters should support adjustable fermentation time and temperature, blending systems should have independent flavor dosing devices, and multi-stage filtration systems should accommodate the selection of different membranes or cartridges based on product requirements. A flexible production system not only improves R&D efficiency but also helps companies quickly respond to market trends.
Choosing an Equipment Supplier with Service Capabilities
Kombucha equipment is not just a one-time purchase; it is a critical asset that companies rely on for long-term operations. When selecting an equipment supplier, companies should evaluate their technical support capabilities, training services, spare parts availability, responsiveness, and remote assistance capabilities. A quality equipment supplier should provide comprehensive services, from workshop layout design and process optimization to equipment installation and commissioning, personnel training, and after-sales maintenance. Furthermore, suppliers with industry experience can often provide practical advice on fermentation parameters and flavor stability control, helping companies quickly enter stable mass production and reduce trial-and-error costs.
Avoiding Common Equipment Purchasing Mistakes
In real-world projects, we often see companies making misjudgments in equipment selection. For example, some companies directly adapt beer equipment for kombucha brewing, ignoring the structural differences between aerobic kombucha fermentation and anaerobic beer fermentation, resulting in process incompatibility. Some startups, driven by budget constraints, purchase inexpensive equipment that lacks CIP cleaning, resulting in frequent contamination incidents and impacting product consistency. Therefore, companies should take a long-term approach when selecting equipment, considering not only procurement costs but also operational efficiency, maintenance requirements, and compliance risks.
Consider environmental protection and energy-optimized design.
Under the “dual carbon” policy and green manufacturing trends, energy efficiency and environmental friendliness of equipment systems are also key considerations in equipment selection. It is recommended to choose equipment equipped with high-efficiency variable-frequency motors, heat recovery systems, and intelligent energy management modules to effectively reduce energy consumption and operating costs. Furthermore, adequate wastewater treatment facilities (such as a fermentation wastewater neutralization system) are crucial for complying with environmental regulations. In plant design, recycling water systems and natural ventilation should be prioritized to reduce carbon footprint and enhance corporate social responsibility.
Common Equipment Selection Mistakes:
- Assuming alcohol/beer equipment is universal: Kombucha ferments aerobically, unlike beer’s anaerobic fermentation. Fermentation tanks have different gas exchange structures and higher hygiene requirements, so avoid copying them.
- Neglecting cooling and fermentation environment control: Many startups neglect refrigeration systems, resulting in excessive fermentation in the summer, flavor variations, and serious product consistency issues.
- Overinvesting in filling equipment: During initial pilot production, it’s not advisable to invest in a large, high-speed filling line all at once. Semi-automatic or small, fully automatic equipment should be prioritized to reduce risk.
Scientifically Selecting Kombucha Equipment
Although the kombucha industry is still in its growth phase, competition is increasingly fierce. Scientifically configured equipment not only ensures food safety and flavor stability but also plays a crucial role in sustainable expansion and brand building. As a kombucha equipment manufacturer, Micet Group recommends that companies scientifically configure equipment based on their production goals, budget, and stage of development. Furthermore, we recommend selecting a partner with process optimization capabilities, installation and commissioning experience, and a comprehensive after-sales service system. Choosing the right kombucha equipment is the first step to successful brewing.