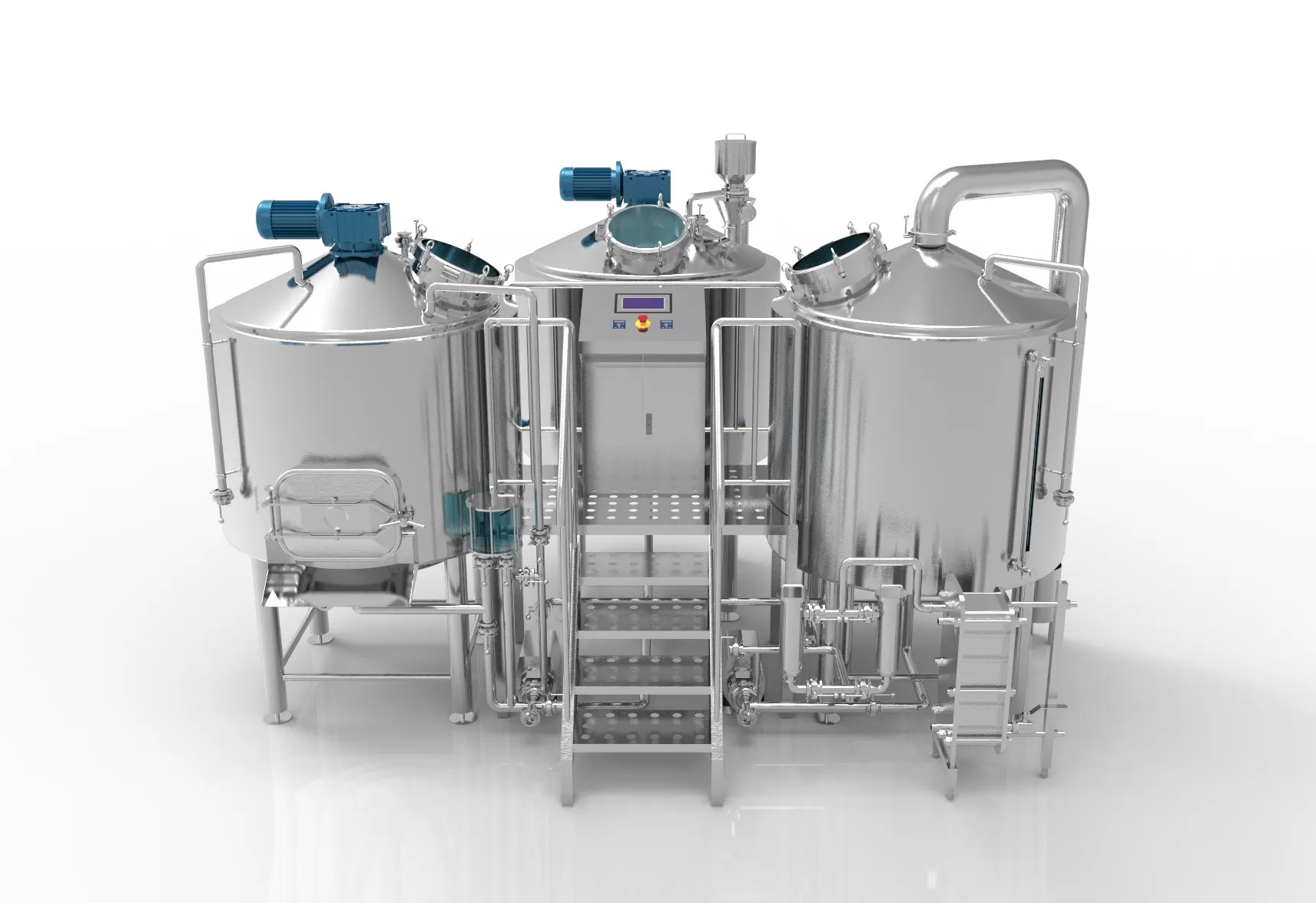
長い間、ワインは世界の文化の中核を担ってきた。蒸留ワインは、ワイン中のアルコールを加熱によって蒸発させ、より高いアルコール濃度に再凝縮するプロセスである。伝統的なワイン醸造とは異なり、蒸留の目的はアルコール分を抽出して濃縮することであり、通常はワイン・スピリッツ(ブランデーなど)の製造などに用いられる。初心者やワイン製造に携わるワインメーカーにとって、蒸留を理解することは非常に重要である。 蒸留装置。 このガイドでは、ワインメーカーがより良いワインを造るために必要な、ワインの造り方と必要な蒸留装置について説明する。
蒸留ワインとは何か?
蒸留ワインとは、アルコール濃度を高めるために加工されたワインのことである。ワインのアルコールは発酵によって生成される。ワイン用ブドウは破砕して果汁を抽出し、ワインメーカーはこれをブドウ果汁と呼ぶ。ブドウ果汁には糖分が含まれており、酵母を加えるとアルコールに変化する。
However, when the alcohol concentration is too high, yeast cannot survive, which naturally limits the concentration of fermented wine. This is why you can’t find ordinary wine with an alcohol content of more than 16%. To make beverages with a higher alcohol content, the wine must be distilled.
ワインに含まれるアルコールはエタノールと呼ばれ、水よりも沸点が低いという便利な性質を持っている。ワインを加熱すると、アルコールは他の成分と一緒に蒸発するが、水は液体のまま残る。蒸留器という簡単な装置を使えば、蒸発したアルコールを水から分離することができる。その結果、蒸留されたワインは元のワインよりもはるかに強いものになる。
ワインの蒸留過程で抽出されるのはエタノールだけではない。芳香化合物、揮発性酸、コンジェナーなど、他の要素も蒸留液に含まれる。これらの要素が最終製品の香り、味、口当たりを決定する。

ワイン醸造プロセス
ブドウの破砕とステミング
ブドウを収穫した後、次のステップは破砕である。破砕の目的は、ブドウの果皮と果汁を分離し、ブドウ果汁を取り出すことである。伝統的には、破砕は歩いて行うことができるが、現代のワイナリーでは一般的に機械式破砕機を使用している。赤ワインの場合、ブドウの皮は色とタンニンを抽出するために果汁と一緒に発酵させるが、白ワインの場合は通常、ブドウの皮を取り除き、果汁だけを残して発酵させる。
破砕後、除梗も必要である。除梗の目的は、ブドウの茎を取り除き、そこに含まれる苦味物質や不要な風味成分がワインに入るのを防ぐことである。除梗することで、ワインの味と風味が向上し、より爽やかでバランスのとれたワインになる。
発酵
発酵はワイン醸造の過程で最も重要な段階のひとつである。この工程では、ブドウ果汁の糖分が酵母によってアルコールと二酸化炭素に変換され、その他の重要な風味物質が生成される。発酵の温度、時間、酵母の選択は、最終的なワインの風味に大きな影響を与える。
- 赤ワインの発酵:赤ワインは通常、ブドウの皮を使って発酵させるため、ブドウの皮に含まれる色素、タンニン、風味物質が抽出されやすくなる。赤ワインの発酵は一般的に、色素とタンニンの抽出を促進するために高温で行われる。
- 白ワインの発酵白ワインは通常、ワインのフレッシュさと酸味を保つために低温で発酵させる。ワインが透明で軽い味わいになるように、ブドウの皮は一般的に取り除かれる。
プレス
発酵が終わると、特に赤ワインの生産では圧搾が必要となる。圧搾の目的は、発酵したブドウの果皮から残りの果汁を抽出し、ワインの生産量を最大にすることである。圧搾の際、ワインメーカーは過度の圧搾と苦味成分の放出を避けるよう注意する必要がある。白ワインの場合、果皮を果汁と一緒に発酵させる必要がないため、圧搾は通常発酵前に行われる。
老化と成熟
ワインの熟成・熟成プロセスとは、ワインを容器に入れ、さらに発酵させたり、寝かせたりして、ワインをよりまろやかで複雑なものにすることである。この段階の長さと容器の選択は、ワインの風味に大きな影響を与える。
- 樽熟成:多くの赤ワインと一部の高級白ワインはオーク樽で熟成される。オーク樽はワインにバニラ、スモーク、ローストなどの独特の風味を与え、樽の通気性はワインの酸化を助け、ワインのタンニンを和らげる。
- ステンレスタンクでの熟成フレッシュな味わいとフルーティーな風味を維持する必要がある白ワインの場合、多くのワインメーカーは熟成にステンレスタンクを選ぶ。ステンレス・タンクは、ワイン本来の風味を最大限に保つことができる。
ろ過と清澄化
熟成後、ワインは通常フィルターにかけられ、清澄化される。この工程の目的は、ワイン中の固体粒子、酵母の沈殿、その他の不純物を取り除き、ワインの透明度と安定性を確保することです。一般的なろ過方法には、ろ紙、活性炭、微多孔フィルターなどがある。
ボトリングと販売
最後のステップは、熟成したワインを瓶詰めすることである。瓶詰め後もワインは熟成を続けることがあり、特に一部の高級赤ワインは通常、瓶の中で長期間熟成させる必要がある。瓶詰め後、ワインは一定の貯蔵期間を経て、最良の飲み頃になるまで熟成され、市場に出回る。
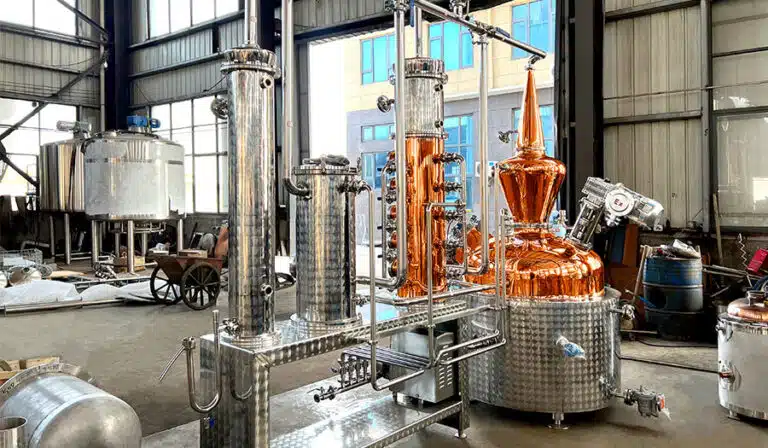

蒸留ワインにはどのような醸造設備が必要ですか?
クラッシャー
除梗したブドウを破砕し、果肉と果汁を分離する。破砕機は通常、回転ドラムやローラーを使って破砕し、ブドウの風味を保ちながら果汁がスムーズに流れ出るようにする。
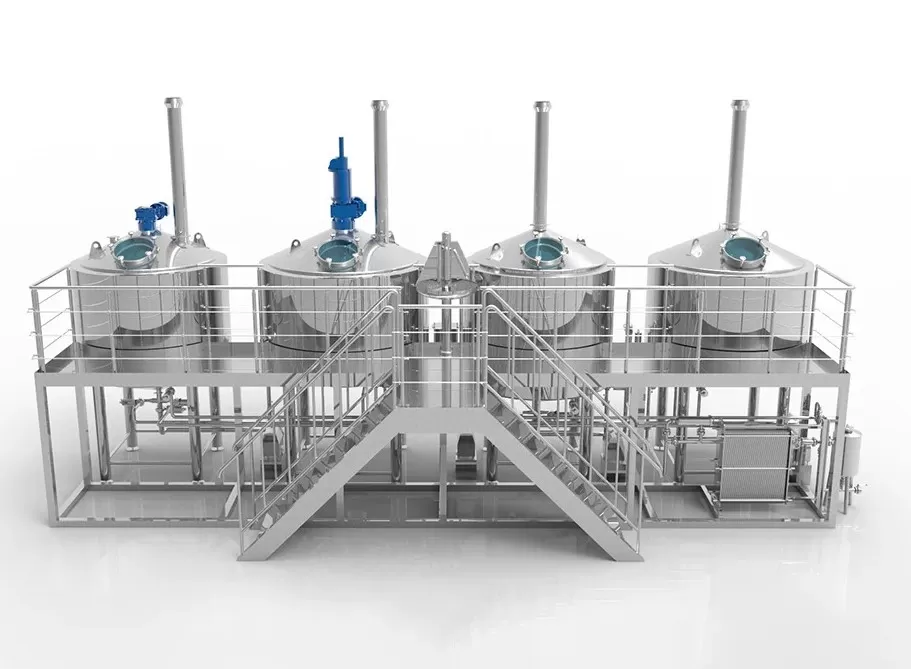
発酵設備
現代のワイン生産では、ステンレス・スチールを使用することが多い。 発酵タンク優れた密閉性を持ち、酸化を防ぎ、ワインの純粋な味を保つことができる。また、ステンレススチールはお手入れも簡単です。
プレス設備
- 縦型プレス:通常、白ワインの生産に使用され、垂直方向に圧力をかけてブドウを絞り、ブドウ果汁を抽出する。縦型プレスは通常、グリッドの付いた円筒形の構造になっている。ブドウをグリッドに押し込んだ後、圧力をかけて果汁を絞り出す。
- 横型プレス:赤ワインの製造によく使われ、水平圧力によってブドウ果汁と果皮を分離するもので、大量生産に適している。最新の横型プレスは通常、圧力を均一かつ正確に制御できる油圧システムを備えている。
ディスティラー
- ポット:通常、ステンレス鋼、銅、またはその他の高温で耐腐食性のある素材でできている。ポット本体はワインを均一に加熱でき、同時に密閉性が高く、アルコールガスが逃げないようにする必要がある。
- 加熱源:伝統的に、追加ポットは直火、蒸気、電気ヒーターで加熱することができる。現代のほとんどの追加加熱装置は蒸気加熱を使用し、より正確に温度を制御し、直接加熱によって引き起こされる直列接続を避けることができます。
- 蒸気:パイプラインから蒸発したアルコールは、蒸気パイプラインを通って凝縮装置に送られる。パイプラインの設計は、伝送の過程でアルコール蒸気が過冷却されたり漏れたりしないようにしなければならない。
コンデンサー
コンデンサーの機能は、蒸発したアルコール蒸気を冷却して液化することである。通常、長い管か蛇行した管で構成され、2層の外管の間に冷却水を流し、アルコール蒸気の温度を効果的に下げ、再び液体に凝縮するのを助ける。
フラクチャリングタワー
フラクショネーターは、異なる成分を分離するための装置であり、特に異なる濃度のアルコールを分離する必要がある蒸留工程で使用される。蒸留ワインの場合、フラクショネーターの機能は、アルコール成分を正確に分離し、水分、糖分、フレーバー物質などの他の不純物を除去することである。分留塔は通常、複数の分留トレイまたはあらかじめセットされた塔で構成されている。アルコール蒸気は塔内を上昇し、徐々に冷却されて成層化し、最終的に異なる出口から濃度の異なるアルコールを回収する。
蒸留温度制御システム
アルコールの蒸発と分留には特定の温度範囲が必要なため、加熱・冷却時の温度制御は極めて重要である。温度制御システムには通常、温度センサー、加熱装置、冷却装置が含まれ、加熱・冷却時の温度制御を正確に行うことができる。
フィルター
ワインを補充する過程で、浮遊物、沈殿物、不溶性物質など、少量のワインがアルコール蒸気とともに持ち出され、最終的なワインの品質に影響を与えることがある。ワインの補充において清澄化と除去を確実にするために、フィルターによる処理が必要となる。
保管と老朽化設備
蒸留されたワイン・アルコールは、一般的にそのまま発酵させるのではなく、最高の風味になるまでさらに貯蔵、ブレンド、熟成させる必要がある。このとき、リザーブ・バレルやオーク樽などの容器を熟成に使用すると、アルコールの味わいや重層性が高まる。
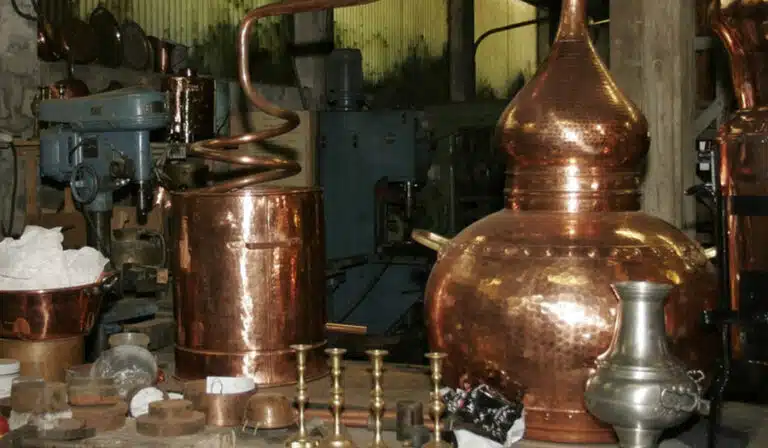

ワイン蒸留装置の選び方
蒸留の目的とアルコールの種類を明確にする
蒸留装置の選択は、まず生産目標に基づいて決定されるべきである。ワイン・スピリッツの種類(ブランデー、ワイン蒸留酒など)によって、蒸留工程に求められる条件は異なる。高純度アルコールが目的であれば、不純物を効率よく除去するために多層式蒸留塔や高精度蒸留釜を装備する必要があるかもしれない。ワインの風味や香りを保持することが目的(ブランデーの醸造など)であれば、銅製の伝統的な蒸留器の方が良いかもしれません。銅は有害な硫化物を除去し、ワインの香りを保持することができるからです。
正しい蒸留釜の素材を選ぶ
蒸留釜の材質は蒸留効果に直接影響します。銅製の蒸留釜は、熱伝導性と化学反応性に優れているため、高級アルコールの蒸留によく使用される。効果的に硫化物を除去し、ワインの品質を向上させることができる。ステンレス製の蒸留釜は、耐食性が強く、耐久性と清潔性に優れているため、大規模生産に適している。生産規模や製品の位置づけによって、適切な素材を選択する必要がある。
生産規模と設備能力を考慮する
蒸留装置の容量は生産規模に応じて選択する。小規模で手作業で生産する醸造所では、生産工程を柔軟にコントロールするために容量の小さいスチル(50L~500L)を選択するのが適しています。大規模な醸造所や工業生産の場合は、効率的な生産のニーズを満たすために、より大きな容量のスチル(500L以上)が必要になる場合があります。適切な設備容量により、生産効率を効果的に向上させ、エネルギーの無駄を省くことができる。
温度制御システムとコンデンサーの設計
蒸留プロセスには正確な温度管理が不可欠です。蒸留工程では、成分によって沸点が異なるため、アルコールと不純物の分離を確実にするためには、正確な温度管理が必要です。デジタル温度制御システムを備えた機器を選択すれば、スチルとコンデンサーの温度をリアルタイムで監視し、加熱パワーを自動的に調整することができます。さらに、凝縮器の設計も同様に重要です。凝縮効果はアルコール還流の効率を直接左右するので、凝縮性能に優れ、冷却システムが完備された装置を選ぶ必要があります。
機器の洗浄とメンテナンスの利便性
機器の洗浄とメンテナンスは、長期使用における重要な要素です。分解や洗浄が容易な機器を選ぶことで、メンテナンスの難易度を下げ、ワインの品質に影響を与える不純物の蓄積を避けることができる。銅製の器具は洗浄に特別な注意が必要だが、ステンレス製の器具は通常、耐久性に優れ、洗浄も簡単だ。加えて、機器の耐食性も重要な考慮点です。長期間使用しても錆びにくく、劣化しにくい機器は、メンテナンスコストを大幅に削減できる。
予算と投資収益率
蒸留装置によって価格差は大きい。選ぶときは予算に応じて合理的に決める必要がある。高級銅製蒸留釜は通常より高価ですが、ワインの香りをよりよく保持でき、高品質のワイン生産に適しています。ステンレス製の機器は比較的安価で、大規模生産に適している。設備を選ぶ際には、エネルギー消費量やメンテナンス費用など、長期的な運転コストも考慮し、設備投資が相応のリターンを得られるようにする必要がある。
サプライヤーとアフターサービス
最後に、評判の良い機器サプライヤーを選ぶことが非常に重要です。良いサプライヤーは、高品質の機器を提供するだけでなく、タイムリーな技術サポートとアフターサービスを提供します。選ぶ際には、他の醸造所の評価を参考にして、設備の安定性とサプライヤーのサービス品質を理解することができます。アフターサービスが充実していれば、生産中断を避けるため、使用中の設備の問題を迅速に解決することができます。