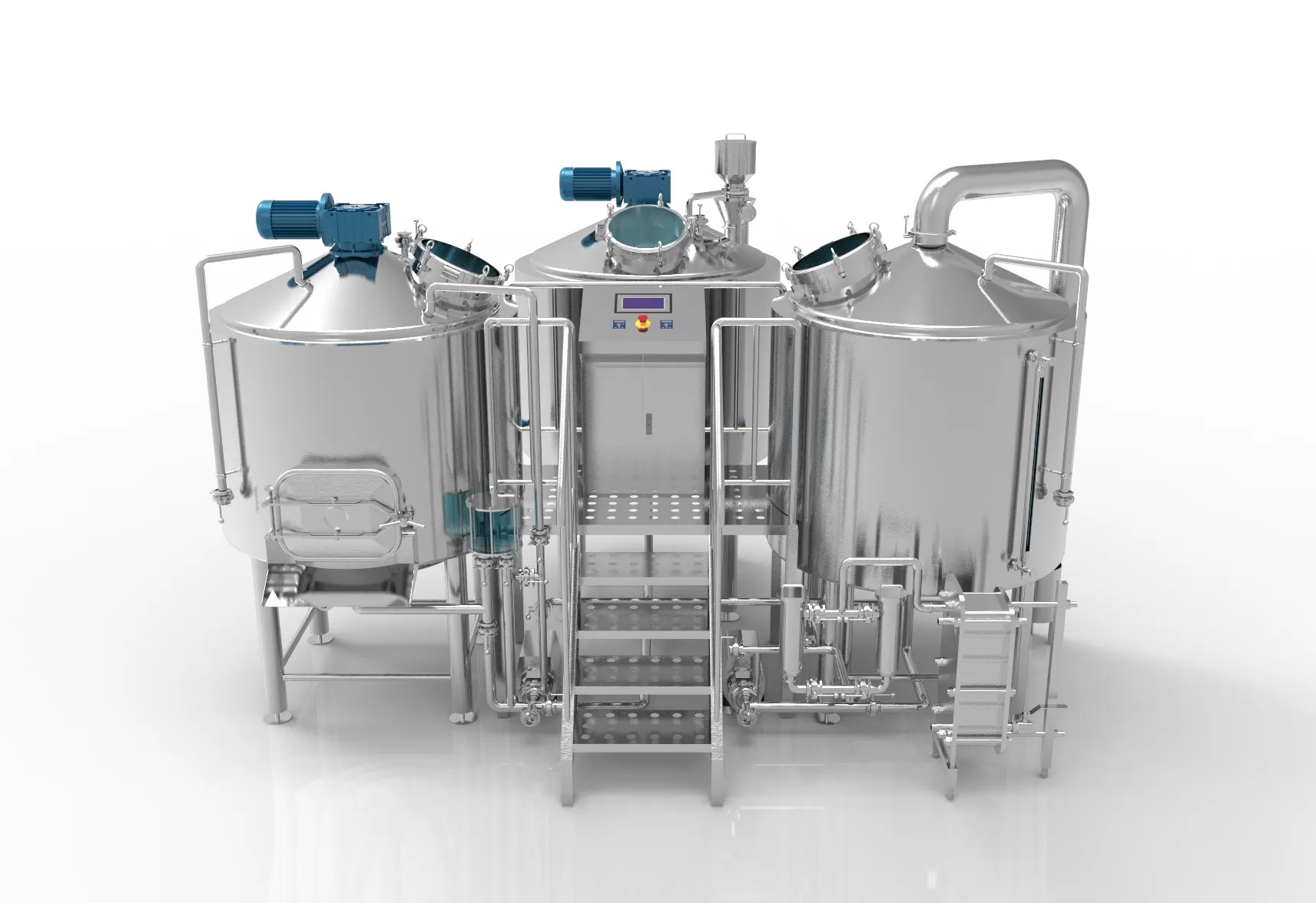
The production of beer requires strict processes, including the use of some systems, including a temperature control system, which can be used to control a good production temperature, which is beneficial to production. Controlling the temperature of fermenting wort can have a significant impact on the flavor of the finished beer. Fermentation above normal temperature ranges may produce excess fruity esters or pungent fusel alcohols. A batch of ale was brewed during the summer and fermentation temperatures were allowed to exceed 80 °F (27 °C). The finished beer tastes like a batch of juicy fruit gum! To achieve consistency from batch to batch and produce results that match the beer style, regulating the temperature in the fermenter is critical. If it’s too hot, it can create off-flavors that ruin the flavor you’re trying to achieve.
What is beer fermentation?
The beer fermentation process is an important step in beer brewing. Fermentation is the chemical conversion of fermentable sugars, with yeast converting glucose in the wort into ethanol and carbon dioxide gas (CO2), which gives beer its alcohol content and carbonation. The fermentation process begins when the cooled wort is transferred to the fermentation vessel and yeast is added.
Two types of fermentation:
- Primary fermentation: The fermentation process begins with the first stage. This is when the brewer’s yeast begins to ferment. Beers usually ferment for about two weeks, but this depends on the beer style.
- Secondary fermentation: Secondary fermentation occurs when a brewer transfers beer from the primary fermentation vessel to a vessel other than the one used to start the fermentation process. If you want the beer to ferment and age for a longer time and you are worried about the yeast settling time being too long, secondary fermentation is crucial.

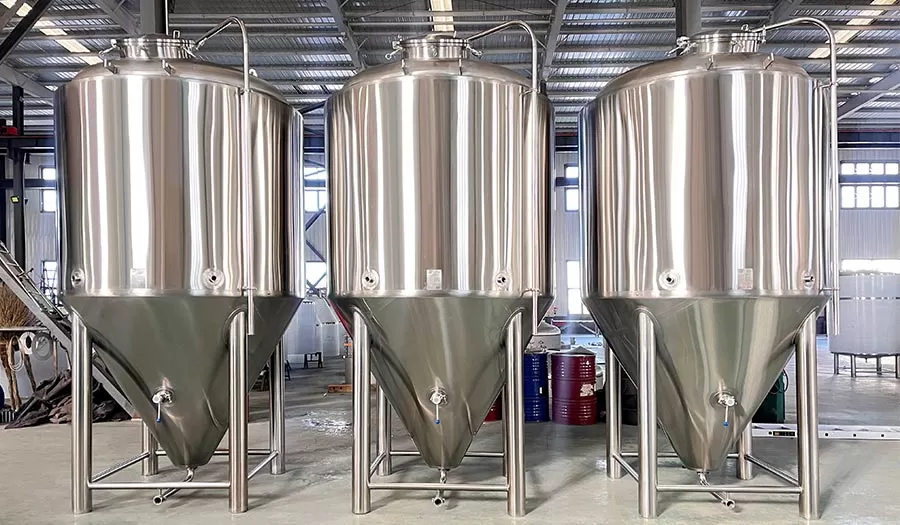
Key components of beer fermentation equipment
Fermentation container
These are the tanks where the wort and yeast are placed to begin the fermentation process. They come in a variety of sizes, from small home brewing setups to large industrial tanks.
Airlock
The airlock allows carbon dioxide (produced during fermentation) to escape from the container without letting any contaminants in.
Temperature control system
Fermentation temperature has a significant impact on the taste of your beer. Many breweries use temperature control systems to ensure beer is fermented at the desired temperature.
The importance of temperature control and monitoring during beer Fermentation
The beer fermentation process requires precision and accuracy. If the temperature is not properly controlled during fermentation, the flavor of the beer will be greatly affected. Fermentation is at the heart of beer brewing. There is no alcohol in unfermented beer. Many of the flavors we associate with beer will be lost. The beer will remain sugary and non-carbonated.
The role of yeast in fermentation
The yeast strain used to ferment beer plays an integral role in creating the desired end product. Different varieties of yeast are used to brew different styles of beer, from ales to lagers. The type of yeast also affects the flavor of the finished beer. Since yeast is a living organism, it needs to be kept at an optimal temperature for successful fermentation. Ale yeast should be stored between 68-72 degrees Fahrenheit, while lager yeast should be stored between 45-55 degrees Fahrenheit.
Monitoring temperature during fermentation
Brewers have several options when it comes to monitoring and controlling temperature during fermentation. The most basic method involves checking the temperature throughout the day (or night) using a thermometer placed inside each fermenter. To achieve more accurate results and increase efficiency, breweries use cooling systems, such as glycol jackets or cooling plates connected to the fermentation tanks, to maintain a constant temperature within each tank without the need for manual input.
Temperature control during fermentation
Fermenting beer at the right temperature helps yeast convert sugar into alcohol, resulting in a delicious beer with a rich flavor. If the temperature is too high or too low, yeast strains can become sluggish or die completely, preventing them from working .
Cold temperatures can also cause beer to become more acidic, while hot temperatures can cause beer to develop off-flavors such as esters and fusel oils. Thus, it is important to pay close attention to the fermentation temperature of your wort throughout the brewing process.
Check temperature changes
To check fermentation temperature, you need some kind of device that can measure fermentation temperature and . The most popular option is a thermometer probe that attaches to the fermenter.
This type of device allows you to track changes in temperature over time so that you can make adjustments if necessary.

What are the temperature control methods for fermentation tanks?
Use a refrigerator or freezer
The benefit of using a refrigerator is its insulation, which helps maintain a consistent temperature. To cool it down, plug it in until it reaches your preferred temperature level.
Evaporation
The evaporation process is used in small conical fermenters. This means that a small stainless steel fermenter can be covered. It provides constant cooling, but you can add a fan if you need to increase its performance.
Brew belt
A brew belt is a power tool that wraps around the fermenter. To use it, you need to plug in the power and heat the steel fermenter to a temperature above room temperature. Additionally, you can install a temperature-sensing unit inside the fermenter that can get out of the brewing zone once the temperature is optimal.
Benefits of temperature control and monitoring during beer fermentation
Temperature control and monitoring during beer fermentation is very important as it helps maintain a consistent environment throughout the brewing process. This allows brewers to produce a consistent product every time without having to worry about flavor changes due to temperature fluctuations.
Additionally, it helps ensure the yeast functions by providing an ideal environment for yeast growth and activity.