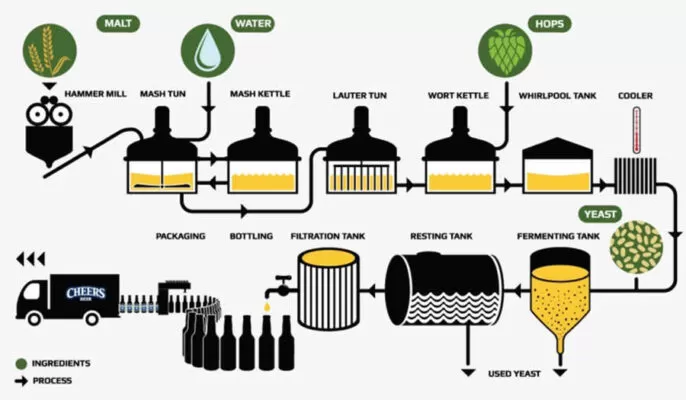
Beer is more than water, hops, malt, and yeast. During beer brewing, various ingredients are mixed, processed, and sometimes the structure of the raw materials is changed. The purpose of the whole process is to convert the grain starch into sugar, which is extracted with water and then fermented by yeast to make an alcoholic carbonated drink. From fresh barley to finished beer we describe these steps in more detail.
Malt
The first step in beer production is malting. Fresh barley is first soaked in water and then germinated in so-called germination boxes. Malted barley is barley grain that has begun the germination process. The malting process is done so that the enzymes necessary to convert the starches in the grain to sugars are formed in the grain. bred barley varieties are used to make malt. Other important characteristics are yield, even germination, ability to produce enzymes and extractable malt.
Milling
The second step in the brewing process is milling. The finished malt is milled, like how flour is made, to dissolve better in water. The aim is to keep the shell intact while breaking the brittle modified starch into granules.
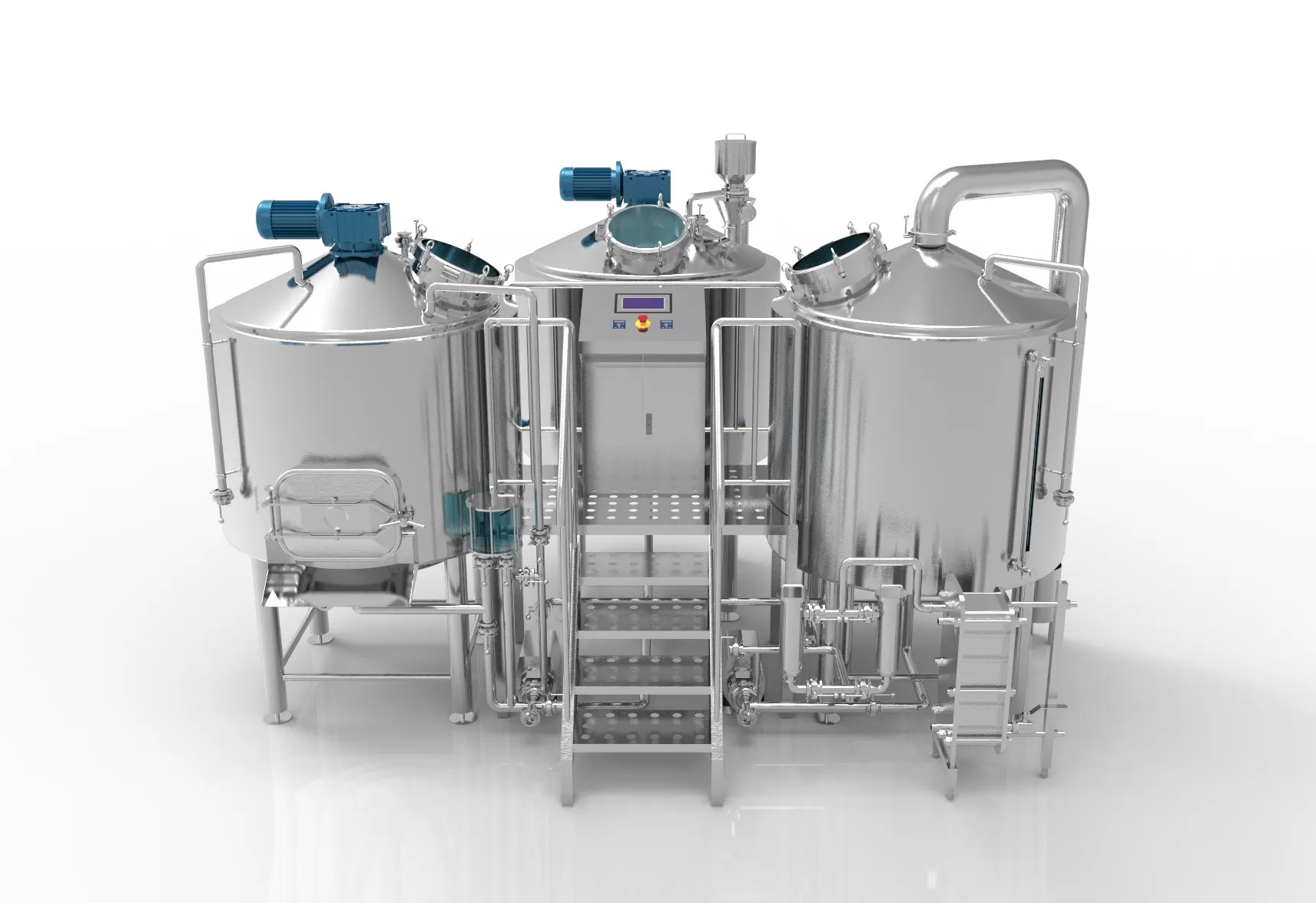
Brewhouse
Brewhouse is brewers’ term for the hot water steeping process. The process hydrates the barley, activates malting enzymes, and converts the grain starch into fermentable sugars. Brewers watch the temperature of the mash very . The sugars produced by the enzymes can be controlled by raising and lowering the temperature.
Filter
Filtration is the process of brewing beer in which the mash is separated into two forms; the remaining grains and the sugary clear liquid called wort. The mash is filtered in the lauter tun, the wort sinks, and the wort is separated from the spent grains.
3 steps of filtering:
- MashOut makes filtration easier by increasing the temperature of the mash. The hotter the mash, the lower the viscosity of the entrained wort and the easier it is to drain from the grain solids.
- Recirculation: Wort is sucked from the bottom of the mash and added to the top
- Jetting: water is added during straining to extract more fermentable sugars from the grain
Boiled
After separation, the wort is transferred to a vessel called a kettle or copper and boiled, which is necessary to inhibit enzyme activity and get added hop bitterness. After the wort has been separated from the grain by filtration, it is boiled for a long time. This is twofold. First, boiling sterilizes the beer.
As the water evaporates, the wort is concentrated into raw wort, the malt enzymes are deactivated, and tannins and protein elements are separated to form what is known as wort.
Fermentation
Fermentation takes place in stainless steel fermenters. This is done in fermenters to which special brewer’s yeast is added. Yeast converts maltose into alcohol and carbon dioxide. Once the maltose has fermented, the yeast sinks and is collected. Depending on the type of yeast and the wort preparation used, top-fermented or bottom-fermented beers can be produced.
Brewing yeast has been categorized as “top fermenting” (or “top fermenting”) and “bottom fermenting” (or “bottom fermenting”); Fermented yeast is used for cooler fermentations, which ferment more . As brewing methods changed in the 20th century and conical fermenting vessels became the norm, yeast collection for both strains was done from the bottom of the fermenter.
Package
Beer is available in bottles, cans, and kegs. It is common practice for brewers to force the carbonation of beer before packaging, as carbon dioxide escapes due to the increased pressure during fermentation, which can cause cans to burst.